CHROMIUM
TRANSITION ELEMENT: CHROMIUM GROUP
| Atomic number: | 24 |
| Group numbers: | 6 |
| Period: | 4 |
| Electronic configuration: | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 |
| Formal oxidation number: | +2 +3 +6 |
| Electronegativities: | 1.66 |
| Atomic radius / pm: | 124.9 |
| Relative atomic mass: | 51.9961(6) |
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (FR) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is a very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds are toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. It is produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Chromium is used to make stainless steel; it gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology. The price of 99.98 % pure chromium shot is 744.80 € for 1000 g.
| Density / g dm-3: | 7190 | (293 K) |
| 6460 | (m.p.) | |
| Molar volume / cm3mol-1: | 7.23 | (293 K) |
| 8.05 | (m.p.) | |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | 12.9 | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m-1K-1: | 93.7 |
| Melting point / °C: | 1907 |
| Boiling point / °C: | 2671 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol-1: | 15.3 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol-1: | 341.8 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol-1: | 394.51 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 652.87 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 1590.64 |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 2987.21 |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | 185 |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 0.00005 |
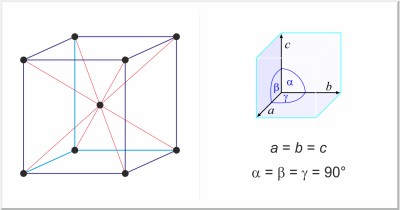
| Crystal structure: | body-centered cubic |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | a=288.46 |
| Space group: | Im3m |
| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 50Cr | 49.946050(1) | 4.345(13) |
| 52Cr | 51.940512(2) | 83.789(18) |
| 53Cr | 52.940654(2) | 9.501(17) |
| 54Cr | 53.938885(1) | 2.365(7) |
| Balanced half-reaction | Eo / V | |
|---|---|---|
| Cr3+ + e- → Cr2+ | - 0.408 | |
| Cr3+ + 3e- → Cr(s) | - 0.744 | |
| Cr2+ + 2e- → Cr(s) | - 0.91 | |
| Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O | +1.33 | |
| Cr2O72- + 12H+ + 6e- → 2CrOH2+ + 5H2O | +1.26 | |
| Cr2O72- + 10H+ + 6e- → 2Cr(OH)2+ + 3H2O | +1.14 | |
| Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 12e- → 2Cr(s) + 7H2O | +0.29 | |
| HCrO4- + 7H+ + 3e- → Cr3+ + 4H2O | +1.20 | |
| CrO42- + 4H2O + 3e- → Cr(OH)3(s) + 5OH- | - 0.13 | |
| HCrO4- + 6H+ + 3e- → CrOH2+ + 3H2O | +1.28 | |
| CrO42- + 7H+ + 3e- → CrOH2+ + 3H2O | +1.40 | |
| CrO42- + 6H+ + 3e- → Cr(OH)2+ + 2H2O | +1.28 | |
| CrO42- + 4H+ + 3e- → CrO2- + 2H2O | +0.95 | |
| CrO42- + 2H+ + 3e- → CrO33- + H2O | +0.36 |
| 23 Vanadium | ← | 24 Chromium | → | 25 Manganese |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Chromium." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. {Date of access}. <https://www.periodni.com/cr.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu
