BORON
BORON GROUP
| Atomic number: | 5 |
| Group numbers: | 13 |
| Period: | 2 |
| Electronic configuration: | [He] 2s2 2p1 |
| Formal oxidation number: | +3 |
| Electronegativities: | 2.04 |
| Atomic radius / pm: | 79.5 |
| Relative atomic mass: | [10.806, 10.821] |
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (GB) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jaques Thénard (FR). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks (Na2B4O7*10H2O). It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Boron is unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. It combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green colour and in rockets as an igniter. The price of 99.5 % pure boron pieces is 997.90 € for 250 g.
| Density / g dm-3: | 2340 | (beta, 293 K) |
| Molar volume / cm3mol-1: | 4.62 | (beta, 293 K) |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | 1.8E+12 | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m-1K-1: | 27 |
| Melting point / °C: | 2075 |
| Boiling point / °C: | 4000 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol-1: | 22.2 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol-1: | 504.5 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol-1: | 557.64 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 800.64 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 2427.09 |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 3659.78 |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | 10 |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 4.8 |
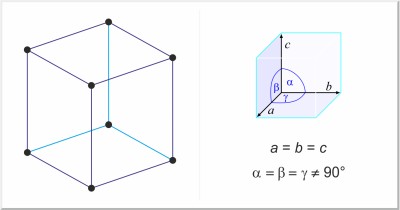
| Crystal structure: | rhombohedral |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | a=506.7, α=58°4' |
| Space group: | R3m |
| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 10B | 10.0129370(3) | 19.9(2) |
| 11B | 11.0093055(5) | 80.1(2) |
| Balanced half-reaction | Eo / V | |
|---|---|---|
| H3BO3 + 3H+ + 3e- → B(s) + 3H2O | - 0.869 | |
| H2BO3- + 4H+ + 3e- → B(s) + 3H2O | - 0.687 | |
| HBO32- + 5H+ + 3e- → B(s) + 3H2O | - 0.437 | |
| BO33- + 6H+ + 3e- → B(s) + 3H2O | - 0.165 | |
| B(OH)3 + 3H+ + 3e- → B(s) + 3H2O | - 0.87 | |
| BF4- + 3e- → B(s) + 4F- | - 1.04 | |
| H2B4O7 + 12H+ + 12e- → 4B(s) + 7H2O | - 0.836 | |
| B4O72- + 14H+ + 12e- → 4B(s) + 7H2O | - 0.792 |
| 4 Beryllium | ← | 5 Boron | → | 6 Carbon |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Boron." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. {Date of access}. <https://www.periodni.com/b.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu
