SILICON
CARBON GROUP
| Atomic number: | 14 |
| Group numbers: | 14 |
| Period: | 3 |
| Electronic configuration: | [Ne] 3s2 3p2 |
| Formal oxidation number: | -4 +2 +4 |
| Electronegativities: | 1.9 |
| Atomic radius / pm: | 117.6 |
| Relative atomic mass: | [28.084, 28.086] |
Silicon was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (SE) in 1824. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word silicis meaning flint. Amorphous form of silicon is brown powder; crystalline form has grey metallic appearance. The solid form is unreactive with oxygen, water and most acids. It dissolves in hot alkali. Silica dust is a moderately toxic acute irritant. Silicon makes up major portion of clay, granite, quartz (SiO2) and sand. Commercial production depends on a reaction between sand (SiO2) and carbon at a temperature of around 2200 °C. It is used in glass as silicon dioxide (SiO2). Silicon carbide (SiC) is one of the hardest substances known and used in polishing. Silicon is by far the more widely used semiconductor for electronics. The price of 99.999 % pure silicon granular is 67.40 € for 1000 g.
| Density / g dm-3: | 2329 | (293 K) |
| 2525 | (m.p.) | |
| Molar volume / cm3mol-1: | 12.06 | (293 K) |
| 11.12 | (m.p.) | |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | 10 | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m-1K-1: | 148 |
| Melting point / °C: | 1414 |
| Boiling point / °C: | 3265 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol-1: | 39.6 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol-1: | 383.3 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol-1: | 451.29 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 786.52 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 1577.15 |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 3231.61 |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | 267700 |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 3 |
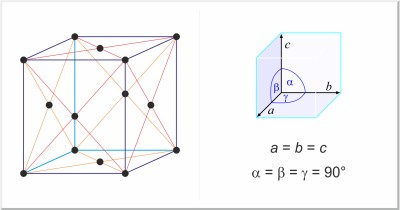
| Crystal structure: | face-centered cubic |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | a=543.07 |
| Space group: | Fd3m |
| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 28Si | 27.976926533(2) | 92.23(1) |
| 29Si | 28.97649472(3) | 4.67(1) |
| 30Si | 29.97377022(5) | 3.10(1) |
| Balanced half-reaction | Eo / V | |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2(s) + 4H+ + 4e- → Si(s) + 2H2O | - 0.86 | |
| SiO32- + 6H+ + 4e- → Si(s) + 3H2O | - 0.455 | |
| HSiO3- + 5H+ + 4e- → Si(s) + 3H2O | - 0.632 | |
| H2SiO3 + 4H+ + 4e- → Si(s) + 3H2O | - 0.780 | |
| SiO2(s) + 8H+ + 8e- → SiH4(g) + 2H2O | - 0.377 | |
| SiO32- + 10H+ + 8e- → SiH4(g) + 3H2O | - 0.176 | |
| HSiO3- + 9H+ + 8e- → SiH4(g) + 3H2O | - 0.265 | |
| H2SiO3 + 8H+ + 8e- → SiH4(g) + 3H2O | - 0.339 | |
| Si(s) + 4H+ + 4e- → SiH4(g) | +0.102 | |
| SiF62- + 4e- → Si(s) + 6F- | - 1.2 |
| 13 Aluminium | ← | 14 Silicon | → | 15 Phosphorus |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Silicon." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. {Date of access}. <https://www.periodni.com/si.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu
