Rn
Radon
RADON
NOBLE GAS
| Atomic number: | 86 |
| Group numbers: | 18 |
| Period: | 6 |
| Electronic configuration: | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 |
| Formal oxidation number: | 0 |
| Electronegativities: | - |
| Atomic radius / pm: | 240 |
| Relative atomic mass: | - |
Radon was discovered by Robert Bowie Owens and Ernest Rutherford (GB) in 1899. The origin of the name is variation of the name of element radium; radon was called niton at first, from the Latin word nitens meaning shining. It is a colourless, odourless radioactive, heavy, noble gas that is chemically inert and non-flammable but is highly radiotoxic and carcinogen by inhalation. Radon is formed from the decay of radium in the earths crust. It is used to treat some forms of cancer.
| Density / g dm-3: | 4400 | (liquid, b.p.) |
| 9.73 | (gas, 273 K) | |
| Molar volume / cm3mol-1: | 50.45 | (liquid, b.p.) |
| 22816.03 | (gas, 273 K) | |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | - | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m-1K-1: | 0.0036 |
| Melting point / °C: | -71 |
| Boiling point / °C: | -61.7 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol-1: | 2.7 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol-1: | 18.1 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol-1: | 0 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 1037.08 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | - |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | - |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | - |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 9E-15 |
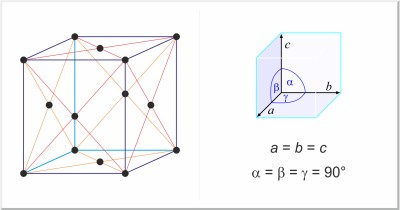
| Crystal structure: | face-centered cubic |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | - |
| Space group: | - |
| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 210Rn | 209.989 69(3) | * |
| 211Rn | 210.990 60(5) | * |
| 222Rn | 222.017 58(2) | * |
| Balanced half-reaction | Eo / V | |
|---|---|---|
| 85 Astatine | ← | 86 Radon | → | 87 Francium |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Radon." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. {Date of access}. <https://www.periodni.com/rn.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu
Copyright © 1998-2025 by Eni Generalic. All rights reserved. | Bibliography | Disclaimer
