CLIMATE CHANGE: DO FOLLOW US GLOBAL WARMING, COOLING OR POLLUTION?
There is only one planet that allows us to live on it
According to the research done by the WWF (World Wildlife Fund) humanity has been living above its capability for years. Our current account is in a deep minus - humanity's ecological imprint in 2007 was 2.7 gha (global hectares) per denizen which is 51 % greater than Earth's combined biocapacity (which amounts to 11.9 billion gha or 1.8 gha per denizen). The ecological footprint gives us a ratio between human demands and the regenerative capability of the biosphere, or in other words it tells us how much of Earth's surface, in global hectares, is required to house our infrastructure (houses, factories, roads,...), to use renewable sources (crops, fish, wood, ...) and to recycle waste (CO2 is currently the only one included). A global hectare is defined as a hectare which has been normalized in a way that its productivity equals the average biological productivity of all the water and land in any given year. As different types of land have different productivity the global hectare of plough-fields encompasses a smaller physical space than a less productive biological plough-field (a "regular" hectare equals 100 m × 100 m or 10 000 m2. "To satisfy the demand of nutrients, energy and other natural recourses we already need a second planet", says Eberhard Brandes from the German branch of WWF. [1]
Following this there are four short, connected stories which won't give you answers to the above stated question, but they may inspire you to become a volunteer on a mission to save our planet. You can find all the references arranged at this page.
- Climate change
- Global warming and mankind
- Story of ozone and ozone holes
- World War 3: Battle for Earth
The climate is changing
With every day we are increasingly confronted with the repercussions of our age-long intent to subject the environment and to adapt it to our needs. Among all ecological topics global warming is the one that claims the most space in media and political discussions. As such we can hear that in the past hundred years, between 1906 and 2006, the average temperature of the Earth's surface rose by 0.6 - 0.9 °C and the rate of the temperature increase almost doubled over the past 50 years. We can also hear that in the 20th century, due to the ice melting, the sea level has risen by 17°cm and the surface of the glaciers all over the world is shrinking just as the surface of the Antarctic ice cover (by 2.7 % annually since 1978). The hole in the ozone layer in April 2011 reached a record height. The average levels of CO2 in 2010 were 389.78 ppm which is more than what was recorded in the previous 420 000 years.
Everyone agrees that the climate is a very complex system and that it's frequently being misinterpreted in various statistics. In an effort to allow you to personally assess what is in store for us, I will try to present the data as objectively as possible in regards to the facts above (and provide links to relevant sites). It isn't my interest to look for people to blame, but my hope is to make at least a few people change their perception of the world around them. Without further ado let's start from the very start and see what climate information the Neanderthals left us.
How can we know what the Neanderthals breathed over 1300°000 years ago?
To answer this question we need to go to Antarctica where near the South Magnetic Pole, on an altitude of 3 488m where a Russian research station, Vostok, is located. From that location (also the place with the lowest measured temperature on Earth, -89.2 °C) ice samples containing the history of the climate spanning 420 000 years in to the past were drilled out from 3623 m deep drilling holes. Right now you are surely wondering what the Antarctic ice has to do with the climate. [2, 3]
How is the Antarctic ice related to the climate?
The Antarctic is the place where in the past few hundred thousand years new snow has been falling on the top of the layer of old snow. So the weight of the new snow compresses the old layers into a compact icy mass in which air bubbles end up trapped. By identifying and counting separate annual layers of the snowy mass (the parallel can be drawn to the process of counting tree rings to determine the tree's age) scientists have found the time of origin for each of the layers. By analyzing the air bubbles trapped in the ice they gained information about the composition of the prehistoric atmosphere, and among other things the amount of CO2 in it. By studying changes in the isotopic system of water from which the ice was made they discovered the air temperature from when the snowflakes formed. The procedure of isotopic fractioning (larger molecules that contain 2H or 18O evaporate slower and condense easier) in the process of changing states is highly dependant on the temperature.
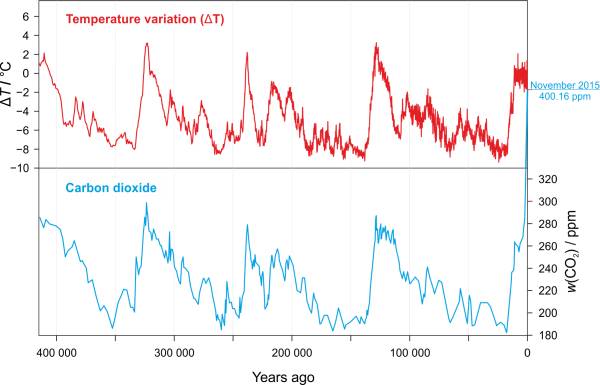
As you can see in Fig. 1 the changes in the concentration levels of CO2 were always followed by equivalent changes in temperature. You can also see that great colds (popularly called ice ages) are usually linked with a very large amount of dust in the air. Why is there dust in the air? It either came from a volcanic eruption, got lifted in to the air by a meteor hitting the Earth or simply got picked up by wind in the dry climate of the ice age. [4]
Fig. 1. Change of temperature and the amount of CO2 on Earth through history - data obtained from ice excavated near the polar station Vostok, Antarctic (EarthLabs, 1999). → Download high quality image
The unusually stable climate of the past 10 000 years (interglacial geological period holocen - the small gray area at the left edge of Fig. 1) aided the development of the human civilization. If we were to look at the figure you would notice that our long warm holocen summer is an exception rather than a rule in the overall cold history of Earth.
After the cold wave which affected various parts of the world, the ice age theory gained in popularity. The theory predicts, contrary to the belief of global warming, that we are heading towards an ice age. One of the world's leading climatologists whose work was used for the UN's report on global warming, professor Mojib Latif from the Leibniz institute in Kiel, believes that we are looking at a 30 cold year period. However, Latif believes that this won't be a lasting trend but a simple pause in the long term process of warming. [5]
What is the cause of global warming?
The changes in the climate system on Earth are affected by numerous interactions between the Sun, oceans, lands, atmosphere and living organisms. The sheer complexity of it is best seen by following weather forecasts. How many of you planned their vacations around weather forecasts? How about picnics? Meteorologist will tell you that in their mathematical models for weather prognosis even a minute change in the most insignificant of parameters can lead to unexpected results. This behavior is in chaos theory known as the butterfly effect: the flap of a butterfly's wings on one part of the world can create stormy weather on the other part.
Scientists are so convinced they are right that it is no surprise they have divided into two uncompromising currents: one side believes that the main culprit for global warming is man while the other believes that it isn't man's fault - it's the nature's.
Man is to blame
Advocates of the anthropogenic (man's) influence of global warming believe that the rise in temperature in the 20th century is mostly the result of human actions. Humanity changes the contents of the atmosphere daily by burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas), by destroying forests, through agricultural activity, etc. while trying to satisfy its need for food, space and energy. [6, 7]
It was discovered long ago that the easiest (some also believe it is the cheapest) way to get rid of atmospheric waste is to eject it directly in to the atmosphere and hope that the wind will carry it somewhere (the further the better). With time it was discovered that this procedure can be improved (distance traveled increased) by building higher chimneys. After intensive research and digging through old scripts scientists were left shocked with the discovery that the part of the waste that we throw into the atmosphere doesn't actually return back to Earth. What followed was a witch hunt against those that ruined the climate and among the first suspects was CO2 (later joined by some other compounds). Since the end of the 19th century when the industrial revolution began, the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere grew by a third, and the process of securing food for several billion people was overloading the atmosphere with methane and nitrous oxide.
Anthropogenesists have concluded that if humanity continues to reduce the transparency of the Earth's atmosphere for infrared radiation the resulting greenhouse effect will catastrophically increase the average temperature of the Earth's surface.
It isn't man's fault - it's the nature's!
On the other hand, the adversaries of the anthropogenic effect on global warming claim that the reasons for climate change are far more complex. They believe that the culprits for the rise of sea temperature need to be sought in natural causes and the activity of the Sun and not in the rise of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
This opposing group is constantly growing, especially after the temperature drop that started in 2008 and the wave of arctic cold which was freezing the homeless all over Europe. A part of the international scientific community, among which are some very reputable names, believe that global warming is just one big delusion behind which stand political and financial interests. Among them is the Croatian academic Vladimir Paar who believes that global warming is a natural occurrence linked to Milankovitch cycle that predicts the coming of a new ice age. The heating and cooling of the Earth are natural processes which have been happening for millions of years, and if we haven't been releasing greenhouse gases we would have already been in an ice age (the last ice age, which cowered around 30 % of the Earth's surface in ice ended around 13 000 years ago). [8]
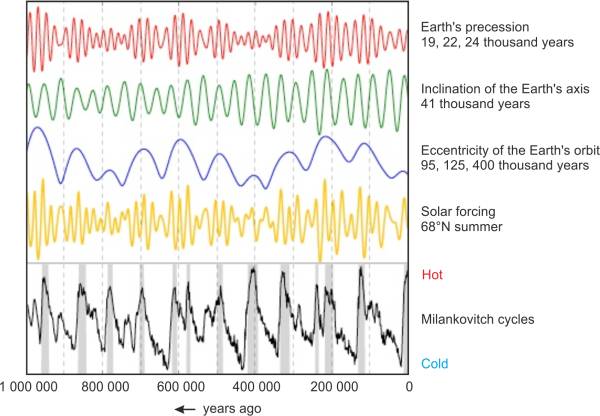
Milankovitch cycles
Fig. 2. Milankovitch cycles, the changes in the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit, the change in the angle and the precession of the Earths rotation axis in the past million years. (Encyclopedia of Earth, 2011). → Download high quality image
The glacial period theory is being talked about more and more often in the climatological and scientific circles. Milutin Milankovic, born in 1879 in Dalj (a place near Osijek, Croatia) developed a mathematical theory that linked climate changes to the changes in the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit and the change in angle and precession of the Earth's rotation axis (Fig. 2). The global change in climate on Earth makes Milankovitch work actual even today. On the 130th anniversary of his birthday UNESCO declared the year 2009 as the Milankovitch year. However, it is worth mentioning that his glacial cycles explain the climate changes extremely well on planets without atmosphere such as Mars, while on Earth the calculations become more complex due to the effect of currents caused by unequal heating of the atmosphere and the oceans. [9]
Sun spots
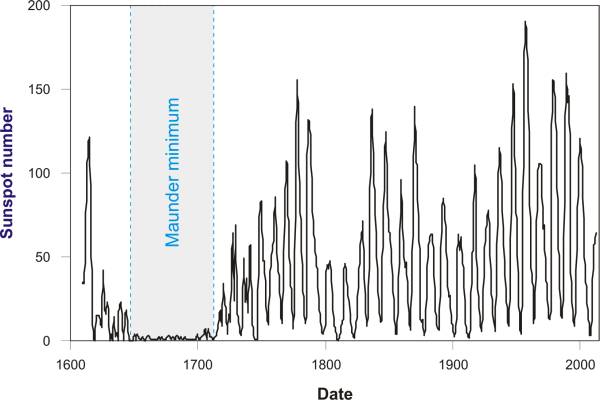
Solar scientists say that we cannot disregard the Sun which is the primary source of energy in our climate system and whose radiation maintains the temperature and with it life on Earth. The number of Sun spots is directly linked to the Sun's activity: measurements have shown that as the number of Sun spots increases, the Sun's radiation also rises. Since the end of the seventies we have been using satellites to measure the radiation emitted by the Sun (TSI, Total Solar Irradiance) during which we have discovered variances of around 0.08 % (or around 1.1 Wm-2) between the lowest and highest value inside the eleven year solar cycle. These changes in the Sun's radiation are too small to explain the unusual climate changes during the 20th century. But the Sun isn't as weak as they may show us. It has other variations and different behavior outside of the eleven year cycle. During one such period, also known as the Maunder's minimum (1645-1715), the number of Sun spots was drastically reduced (look at Fig. 3). That period coincides with the long cold period in Europe that got nicknamed the "little ice age". [10]
Fig. 3. Average yearly number of Sun spots in the past 400 years (NASA, 2011). → Download high quality image
In 2008 and 2009 the Sun spots nearly vanished and solar activity fell. Do you remember what the winter was like then?
"Local" phenomena
It's not only astronomical phenomena that affect the global climate. Even relatively local phenomena such as changes in sea currents or volcanic eruptions can drastically change the climate on the whole Earth.
Peter Wadhams, Professor of Oceanic Physics at the University of Cambridge, and his colleagues believe that they have found the first signs of the Golf current slowing down, as published by The Sunday Times in 2005. They have discovered that one of the main mechanisms that controls the Golf current - the lowering of the column of cold water in the Greenland sea - fell to one fourth of its previous scale. And, despite the global warming, the Golf current stopping could result in the Great Britain and the northwest of Europe being trapped in ice. [11]
The end of 1997 brought great rains and floods in South America (Peru, Ecuador, Chile) and east Africa (Kenya) and drought and forest fires in otherwise damp southeast Asia (Borneo, Sumatra, Malaysia). The culprit was El Niño whose influence was felt even in Europe. El Niño and La Niña are two extremes in the global atmosphere - ocean phenomenon ENOS (El Niño - Southern Oscillation) which represents circulation that happens in the equatorial part of the Pacific Ocean. During the warm phase, El Niño, there is a twist in the prevailing layout of the ocean surface temperature, air pressure, warm circulation in the atmosphere and weather conditions. La Niña is essentially just an extremely expressed normal (cold) phase of ENSO. Even though El Niño has been studied for years, nothing has been found that could explain what exactly triggers this phenomenon. [12, 13]
Even though volcanoes can eject massive amounts of greenhouse gasses in to the atmosphere they are more commonly linked with global freezing rather than warming. The eruption of the volcano Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines in June of 1991 threw out, according to estimates, around 22 tons of sulfur dioxide in to the upper layers of the atmosphere. In combination with the water this created an aerosol cloud of sulfuric acid which reflected the Sun's radiation causing the whole planet to cool down by 0.5 °C during 1992 and 1993 (the maximum was in August of 1992, 0.73 °C). In the historic records there is a mention about a "year without summer" which followed the eruption of the volcano Tambora in Indonesia. [14]
Who to believe?
Since we can't affect natural occurrences let's see what the climatologists say about man's effect on climate changes.
Some will lie for money (privileges, power) while others will present data that support their "truth", the third are exclusive and believe only in their own "truth", the fourth are most likely right but they are lost in all this crowd. Which one of them is actually right, only time will tell (if we end up having enough of it). We have already witnessed cases where someone's interest was above our collective safety - do you remember the "perfectly safe" DDT or asbestos which we used massively up until recently? Now, let us carry on because the more we know the harder we can be tricked!
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Climate change: Do follow us global warming, cooling or pollution?." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. {Date of access}. <https://www.periodni.com/climate_change.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu