COBALT
TRANSITION ELEMENT: COBALT GROUP
| Atomic number: | 27 |
| Group numbers: | 9 |
| Period: | 4 |
| Electronic configuration: | [Ar] 3d7 4s2 |
| Formal oxidation number: | +2 +3 |
| Electronegativities: | 1.88 |
| Atomic radius / pm: | 125.3 |
| Relative atomic mass: | 58.933 194(4) |
Cobalt was discovered by Georg Brandt (DE) in 1739. The origin of the name comes from the German word kobald meaning goblin or evil spirit. It is a hard, ductile, lustrous bluish-grey metal and it's surfaces are stable in air. Cobalt reacts over time with dilute acids and has remarkable magnetic properties. Cobalt occurs in compounds with arsenic and sulfur as in cobaltine (CoAsS) and linneite (Co3S4). Pure cobalt is obtained as a by-product of refining nickel, copper and iron. Cobalt is used in many hard alloys; for magnets, ceramics and special glasses. Radioactive cobalt-60 is used in cancer therapy. The price of 99.9 % pure cobalt pieces is 171.20 € for 500 g.
| Density / g dm-3: | 8900 | (293 K) |
| 7670 | (m.p.) | |
| Molar volume / cm3mol-1: | 6.62 | (293 K) |
| 7.68 | (m.p.) | |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | 6.24 | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m-1K-1: | 100 |
| Melting point / °C: | 1495 |
| Boiling point / °C: | 2927 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol-1: | 15.2 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol-1: | 382.4 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol-1: | 423.082 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 760.41 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 1648.27 |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol-1: | 3232.28 |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | 29 |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 0.0005 |
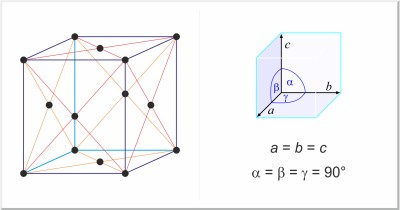
| Crystal structure: | face-centered cubic |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | a=354.41 |
| Space group: | Fm3m |
| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 59Co | 58.933200(2) | 100 |
| Balanced half-reaction | Eo / V | |
|---|---|---|
| Co3+ + e- → Co2+ | +1.808 | |
| Co2+ + 2e- → Co(s) | - 0.277 | |
| Co3O4(s) + 8H+ + 2e- → 3Co2+ + 4H2O | +2.11 | |
| Co2O3(s) + 6H+ + 2e- → 2Co2+ + 3H2O | +1.75 | |
| Co(OH)2(s) + 2e- → Co(s) + 2OH- | - 0.73 | |
| Co(NH3)63+ + e- → Co(NH3)62+ | +0.1 | |
| CoO(OH)(s) + H2O + e- → Co(OH)2(s) + OH- | +0.17 |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Cobalt." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 13 Feb. 2025. Web. 19 Apr. 2025. <https://www.periodni.com/co.html>.
Articles and tables
- Periodic table
- Online calculators
- Scientific calculator for chemists
- Gas laws calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Angle converter
- Roman numerals converter
- Number systems converter
- Preparation of solutions
- Labeling of chemical containers
- Oxidation numbers calculator
- ARS method
- Oxidation number change method
- Ion-electron method
- Gauss elimination method
- Memory game
- Find the pairs
- Articles and tables
- Chemistry
- List of abbreviations and acronyms
- Crystal systems and Bravais lattices
- GHS - Hazard pictograms
- NFPA 704 Hazard Diamond
- Fundamental physical constants
- Solubility product constants
- SI - International System of Units
- Composition of mixtures and solutions
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Chlorinity and salinity of seawater
- Rare earth elements (REE)
- Ecology
- Web design
- Chemistry dictionary
- Chemistry
- Downloads
- ≡ Menu
